Download it for free here:
http://www.codeblocks.org/downloads/26
Open it, choose:
Create a new project → Console application
Open it, choose C++
At School - make a new file in C: to temporarily save your work in:
[...]
Computer - local disk C: - make new folder - codeblocksfiles
Type in a project title (project filename and resulting filename will fill in automatically)
At home: A folder on your desktop might work better
Use all of the defaults for this
Open up Sources→main.cpp
The classic "Hello World" program should already be here for you to do a test build and run with.
First build it by clicking on the yellow gear, then run it by clicking on the green arrow.
Did you get an error? read the error at the bottom of the screen
It can't find the compiler?
Settings→compiler→Global compiler settings→Toolchain executable→ "Auto Detect" compiler's installation directory
just google whatever errors you find, make sure all of the paths are set up correctly.
Once it is set up correctly, it will compile and you will get a black screen with "Hello World" written on it.
Hello World!
For a description of what all of the lines in your first "hello world" code are doing, read this:http://www.cplusplus.com/doc/tutorial/program_structure/
The above website is a great resource to give you some basic preliminary tutorials if you are interested in teaching yourself.
Let's add a little more to your program:
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
// operator order
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
cout<<"Hello World!";
int a, b; // this declares "a" and "b" as being integers that initially have no assigned value
a = 8; // here we assign a the value of 8
b = 2; // now b is assigned a value of 2
a = b; // just a demo of the importance of order, a is now equal to 2,
b = 15; // now a still equals 2, but b has changed to 15.
cout << "\n a:"<< a; //cout writes information out to the screen
cout << "\n b:"<< b<<"\n\n";
}
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
cout<< "for input and output, see";
http://www.cplusplus.com/doc/tutorial/basic_io/
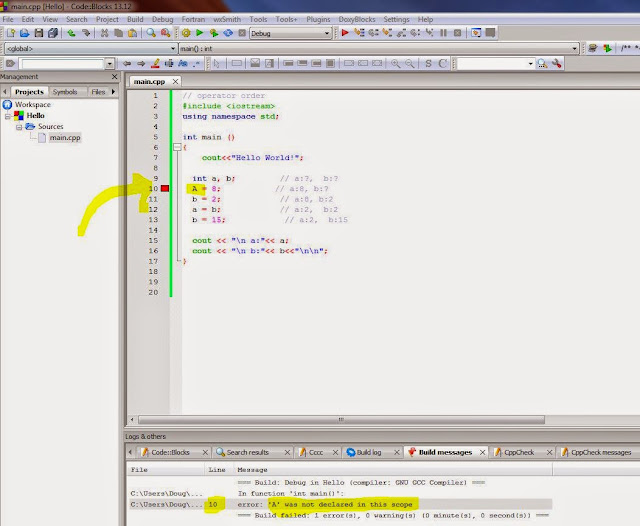
What if there is an error in your code?
Change "a" to "A" and see what happens when you try to build it:
The red square show you where the error is, and your build messages tell you what the problem is. If you do not understand the error message, just gooogle it! In this case, "A" has not been declared - in other words, we did not tell the computer if "A" will store a letter or a number, and if a number what kind of a number - how many bits should it reserve for this information? If I change "a" to "A" above, I will fix the error:
You can call your variables whatever you want, just be consistent!
Now, try this - change the integer "2" to something with a decimal like "2.315" and see what happens:
Note that the output is still the integer "2" even though it is typed into the program as 2.315. If we change the variable b from being an integer to holding more information we will have to declare it as something different than an integer, like float:
A list of different types of variables can be found here:
http://www.cplusplus.com/doc/tutorial/variables/
for, if, while...
http://www.cplusplus.com/doc/tutorial/control/Study this program, and see if you can figure out what it is doing:
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
//Airplane.cpp : Program to demonstrate for statements.
#include "iostream"
int main(void)
{
int count;
for(count=1; count<=500;count++)
std::cout<<"I will not throw paper airplanes in class.";
return 0;
}
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
for (initialization; condition; increase) statement;
The point of computer programs - to perform all of those monotonous repetitive tasks we would rather not deal with!
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
//bottles of beer song lyrics
#include "iostream"
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n, c,count;
cout << "Enter the number of beer bottles you want to start out with" <<"\n";
cin >>n;
c=n+1;
for(count=0; count<=n-1; count++)
{ c -= 1;
cout<<c<<" bottles of beer on the wall "<<c<<" bottles of beer"<<"\n";
cout<<"take one down, pass it around,"<<c-1<<" bottles of beer on the wall"<<"\n";
}
return 0;
}
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
see: http://www.cplusplus.com/doc/tutorial/operators/
Class exercise #1:
Modify the below program to write out the Fibonacci series using a for loop:
Just replace "????" with what it needs to be!
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
//Fibonacci series Program to demonstrate for statements.
#include "iostream"
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n, a=0,b=1,c,count;
cout << "Enter the number of terms of Fibonacci series you want" <<"\n";
cin >>n;
cout<<"1"<<"\n";
for(count=0; count<=n; count++)
{ c = a + b;
a = ????;
b = ????;
cout<<c<<"\n";}
return 0;
}
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Class exercise #2:
Fix the equations in the below program so that it correctly calculates someone's age (slightly different equation if someone has already had their birthday, vs. if they have not had their birthday yet).
Add one more if statement that writes "Happy Birthday!" if currentmonth = birthmonth
// Age Calc.cpp : Program to calculate someone's exact age.
//
#include <iostream>
#include <conio.h>#include <time.h>
using namespace std;
{
int birthmonth,birthyear;int currentmonth,currentyear;
int agey,agem;
cout << "\n\n\t\t\t Age Calculator\n\n";
cout <<"Enter Your Birth Year(Eg:1989):";cin >>birthyear;
cout<<"\n\nEnter Your Birth Month(Eg:7):";
if(birthmonth > 12 || birthmonth < 1)
return 1;
time_t t = time(0); // get time now
struct tm * now = localtime( & t );currentmonth = (now->tm_mon + 1);
currentyear = (now->tm_year + 1900);
{ agey=currentyear-birthyear;
agem=currentmonth-birthmonth;}
{agey=currentyear-birthyear;
agem=currentmonth-birthmonth;}
cout<<"\n\n\t\tYour Age is "<<agey<<" Years And "<<agem<<" Months ";
_getch();
return 0;
}
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Example Codes:
The best way to learn how to program, is to study open source codes.
Can you figure out what each line is doing in the below codes?
Just google terms you do not understand!
//8-ball program - example of using arrays, rand, and strings
#include <cstdlib>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <time.h>
using namespace std;
const int ARRAY_LENGTH = 6;
string eightBall[ARRAY_LENGTH];
bool prgExit = false;
int main()
{
srand ( time(0));
string userInput;
eightBall[0] = "No";
eightBall[1] = "Yes";
eightBall[2] = "Perhaps...";
eightBall[3] = "Most definetly yes";
eightBall[4] = "Almost positively not";
eightBall[5] = "I think so...";
cout << "Welcome to the Magic 8-Ball Game!\n";
cout << "Type a Yes or No question to play, or type 'exit' to quit\n";
while(!prgExit)
{
cout << "\nAsk me a question and I will tell the future!\n" ;
getline(cin, userInput);
if(userInput.compare("exit") == 0)prgExit=true;
if(userInput.compare("") != 0 && userInput.compare("exit") != 0){
cout << eightBall[rand()%ARRAY_LENGTH] << "\n";
userInput = "";
}
}
cout << "Thanks for playing!\n";
system("PAUSE");
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
//hangman game
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <ctime>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
const int MAX_TRIES=12;
int letterFill (char, string, string&);
int main ()
{
string name;
char letter;
int num_of_wrong_guesses=0;
string word;
string words[] =
{
"United States"
"india",
"pakistan",
"nepal",
"malaysia",
"philippines",
"australia",
"iran",
"ethiopia",
"oman",
"indonesia"
};
//choose and copy a word from array of words randomly
srand(time(NULL));
int n=rand()% 11;
word=words[n];
// Initialize the secret word with the * character.
string unknown(word.length(),'*');
// welcome the user
cout << "\n\nWelcome to hangman...Guess a country Name";
cout << "\n\nEach letter is represented by a star.";
cout << "\n\nYou have to type only one letter in one try";
cout << "\n\nYou have " << MAX_TRIES << " tries to try and guess the word.";
cout << "\n~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~";
// Loop until the guesses are used up
while (num_of_wrong_guesses < MAX_TRIES)
{
cout << "\n\n" << unknown;
cout << "\n\nGuess a letter: ";
cin >> letter;
// Fill secret word with letter if the guess is correct,
// otherwise increment the number of wrong guesses.
if (letterFill(letter, word, unknown)==0)
{
cout << endl << "Whoops! That letter isn't in there!" << endl;
num_of_wrong_guesses++;
}
else
{
cout << endl << "You found a letter! Isn't that exciting!" << endl;
}
// Tell user how many guesses has left.
cout << "You have " << MAX_TRIES - num_of_wrong_guesses;
cout << " guesses left." << endl;
// Check if user guessed the word.
if (word==unknown)
{
cout << word << endl;
cout << "Yeah! You got it!";
break;
}
}
if(num_of_wrong_guesses == MAX_TRIES)
{
cout << "\nSorry, you lose...you've been hanged." << endl;
cout << "The word was : " << word << endl;
}
cin.ignore();
cin.get();
return 0;
}
/* Take a one character guess and the secret word, and fill in the
unfinished guessword. Returns number of characters matched.
Also, returns zero if the character is already guessed. */
int letterFill (char guess, string secretword, string &guessword)
{
int i;
int matches=0;
int len=secretword.length();
for (i = 0; i< len; i++)
{
// Did we already match this letter in a previous guess?
if (guess == guessword[i])
return 0;
// Is the guess in the secret word?
if (guess == secretword[i])
{
guessword[i] = guess;
matches++;
}
}
return matches;
}
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
//tic-tac-toe game
#include< iostream>
using namespace std;
void display_board();
void player_turn();
bool gameover();
//bool - true = 1, false = 0
char turn;
bool draw = false;
char board[3][3] = {{'1', '2', '3'}, {'4', '5', '6'}, {'7', '8', '9'}};
//char = character, used for variables that hold letters like "x"
int main()
{
cout << "Tic Tac Toe Game\n";
cout << "Player 1 [X] --- Player 2 [O]\n";
turn = 'X';
while (!gameover())
{
display_board();
player_turn();
gameover();
}
if (turn == 'O' && !draw)
{
display_board();
cout << endl << endl << "Player 1 [X] Wins! Game Over!\n";
}
else if (turn == 'X' && !draw)
{
display_board();
cout << endl << endl << "Player 2 [O] Wins! Game Over!\n";
}
else
{
display_board();
cout << endl << endl <<"It's a draw! Game Over!\n";
}
}
void display_board()
{
cout <<"---------------------" << endl << endl;
cout << " | | " << endl;
cout << " " << board[0][0] << " | " << board[0][1] << " | " << board[0][2] << endl;
cout << "_____|_____|_____"<< endl;
cout << " | | " << endl;
cout << " " << board[1][0] << " | " << board[1][1] << " | " << board[1][2] << endl;
cout << "_____|_____|_____"<< endl;
cout << " | | " << endl;
cout << " " << board[2][0] << " | " << board[2][1] << " | " << board[2][2] << endl;
cout << " | | " << endl;
}
void player_turn()
{
int choice;
int row = 0, column = 0;
if (turn == 'X')
{
cout << "Player 1 turn [X]: ";
}
else if (turn == 'O')
{
cout << "Player 2 turn [O]: ";
}
cin >> choice;
switch (choice)
{
case 1: row = 0; column = 0; break;
case 2: row = 0; column = 1; break;
case 3: row = 0; column = 2; break;
case 4: row = 1; column = 0; break;
case 5: row = 1; column = 1; break;
case 6: row = 1; column = 2; break;
case 7: row = 2; column = 0; break;
case 8: row = 2; column = 1; break;
case 9: row = 2; column = 2; break;
default:
cout << "You didn't enter a correct number! Try again\n";
player_turn();
}
if (turn == 'X' && board[row][column] != 'X' && board[row][column] != 'O')
{
board[row][column] = 'X';
turn = 'O';
}
else if (turn == 'O' && board[row][column] != 'X' && board[row][column] != 'O')
{
board[row][column] = 'O';
turn = 'X';
}
else
{
cout << "The cell you chose is used! Try again\n";
player_turn();
}
}
bool gameover()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)//Check for a win
{
if ((board[i][0] == board[i][1]&& board[i][1] == board[i][2]) || (board[0][i] == board[1][i]&& board[1][i] == board[2][i]) || (board[0][0] == board[1][1]&& board[1][1] == board[2][2]) || (board[0][2] == board[1][1]&& board[1][1] == board[2][0]))
{
return true;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)//Check for draw
{
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++)
{
if (board[i][j] != 'X' && board[i][j] != 'O')
{
return false;
}
}
}
draw = true;
return true;
}
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Create a simple code of your own -
Examples:
grade calculator - enter HW grades, have it add them up and average them
circuits: enter resistor values, calculate voltage drops for a series circuit
Friction: Enter slip angle, calculate friction coefficient - can you find what library file you need to include for this one?