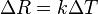Fundamental property of matter - like mass & length.
positive, or negative charge

Ampere current unit
6.241×10^18 electrons (or one coulomb) per second = one ampere
Voltage = electrical potential difference between two points
units = volts = joules / coulomb
Voltage = the work done per unit charge against a static electric field to move the charge between two points.
A voltmeter can be used to measure the voltage (or potential difference) between two points in a system; usually a common reference potential such as the ground of the system is used as one of the points.
Conductor - material that permits the flow of electricity
Resistor - resists the flow of electricity
Ohm (symbol: Ω) is the SI unit of electrical resistance
1 Ohm = the resistance between two points of a conductor when a constant potential difference of 1.0 volt, applied to these points, produces in the conductor a current of 1.0 ampere
Ohm's Law: V = iR
Voltage = Current * resistance
Kirchoff's current law - Conservation of charge
The current entering any point = the current leaving the point
i2 + i3 = i1 + i4
Kirchoff's voltage law - Conservation of energy

The sum of all the voltages around the loop= zero
v1 + v2 + v3 - vin = 0
or
Vin = V1 + V2 + V3
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Resistors in series -

~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Resistors in ParallelData Acquisition & Control
Data Acquisition - take data, like measuring pressure, force, temperature, etc. Writing a number down to represent a physical quantity.
Control - Use electrical outputs to control a physical property (like Temperature, or pressure) in a system.
Thermistor -
A thermistor is a type of resistor whose resistance varies with Temperature
Assuming, as a first-order approximation, that the relationship between resistance and temperature is linear, then:
 = change in resistance
= change in resistance = change in temperature
= change in temperature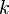 = first-order temperature coefficient of resistance
= first-order temperature coefficient of resistance
Strain gauge: R varies with Strain
(wires get thinner and longer with strain, this increases resistance)

Analog Information - the actual physical voltage that varies proportionately with a physical property such as temperature, or pressure, or sound. Analog signals are smooth, with infinite resolution - not pixilated.
Digital information - the number that shows up on your computer screen to represent the physical voltage. The number on your screen is "pixilated", it does not exactly match the physical entity you are trying to measure.
Analog to Digital Converter - ADC -
Analog-to-digital converter (ADC) is a device which can convert the actual analogue voltage into digital numbers on a multimeter or on a computer.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VBDoT8o4q00
Bits - How a computer stores information.
ADC has n-bit resolution (8 bit, 12 bit, 16 bit, 24 bits etc.) higher-resolution ADC = a smaller step size
Step size = the smallest change between digital numbers
Example: 8 bits, representing 0-5V.
the range is divided into 2^8=256 steps (from 0 – 255)
Step size = 5/(2^N-1) = 5/255 = 0.01961V or 19.1mV
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Charge: electron = 1.602 X 10^-19 coulombs (C)
Fundamental property of matter - like mass & length.
positive, or negative charge
Lab - see D2L